The task at hand was to super-resolve a low-resolution stereo image pair to a high-resolution one with a magnification factor of ×4.Compared with single image SR, the major challenge lies in how to exploit additional information in another viewpoint and how to maintain stereo consistency in the results. This challenge had 3 tracks, including one track on distortion (e.g., PSNR) and bicubic degradation, one track on perceptual quality (e.g., LPIPS) and bicubic degradation, as well as another track on real degradations. We participated in 2/3 tracks and ranked 7 and 13 in track 1 and track 2 respectively.
Stereo Images and their Importance in Research
- Stereo images capture two views of the same scene from slightly different viewpoints, simulating the human visual system binocular vision.
- This difference in viewpoints allows for the calculation of depth information, or disparity, between corresponding pixels in the left and right images.
- This disparity information is used to create a depth map that can be used for a variety of computer vision tasks, such as estimating the position and orientation of objects in 3D space.
- Stereo images provide depth information that is critical for many applications, including scene reconstruction, object detection, tracking, and recognition.
- More desired with the popularity of dual cameras in mobile phones. Stereo images are also used for robotics, autonomous driving, and virtual and augmented reality applications, making them a critical part of computer vision research.
Results Achieved




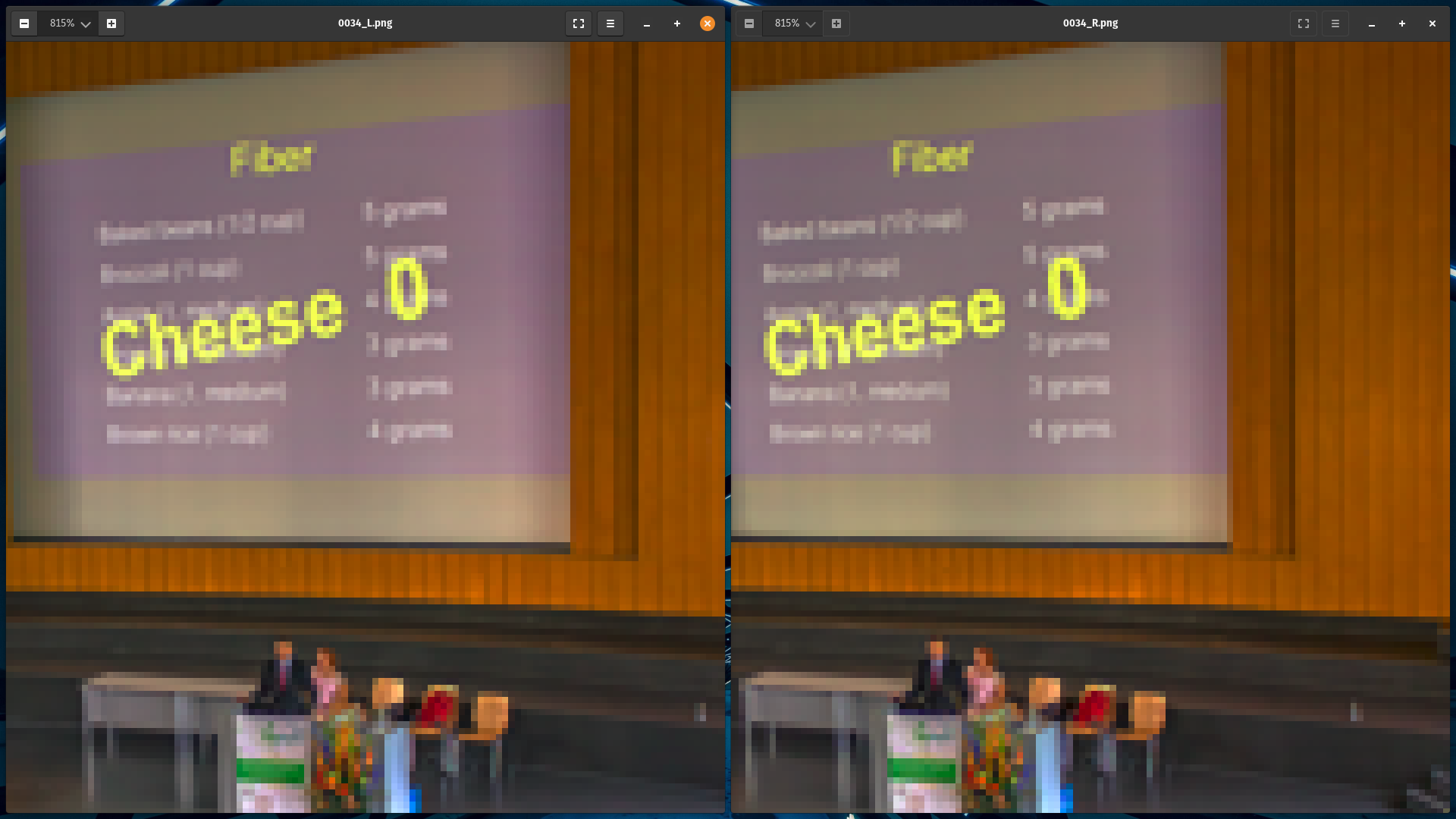
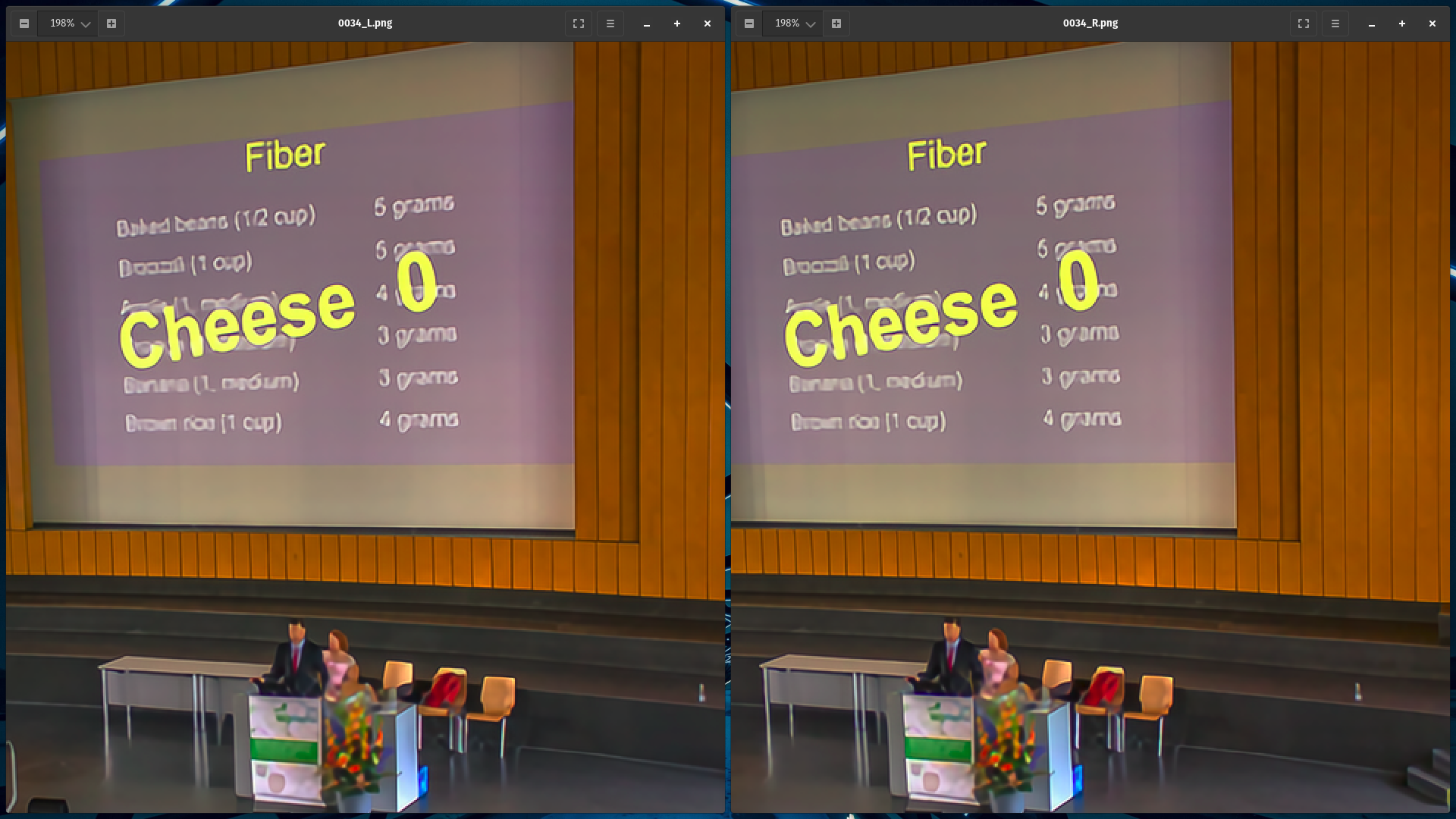
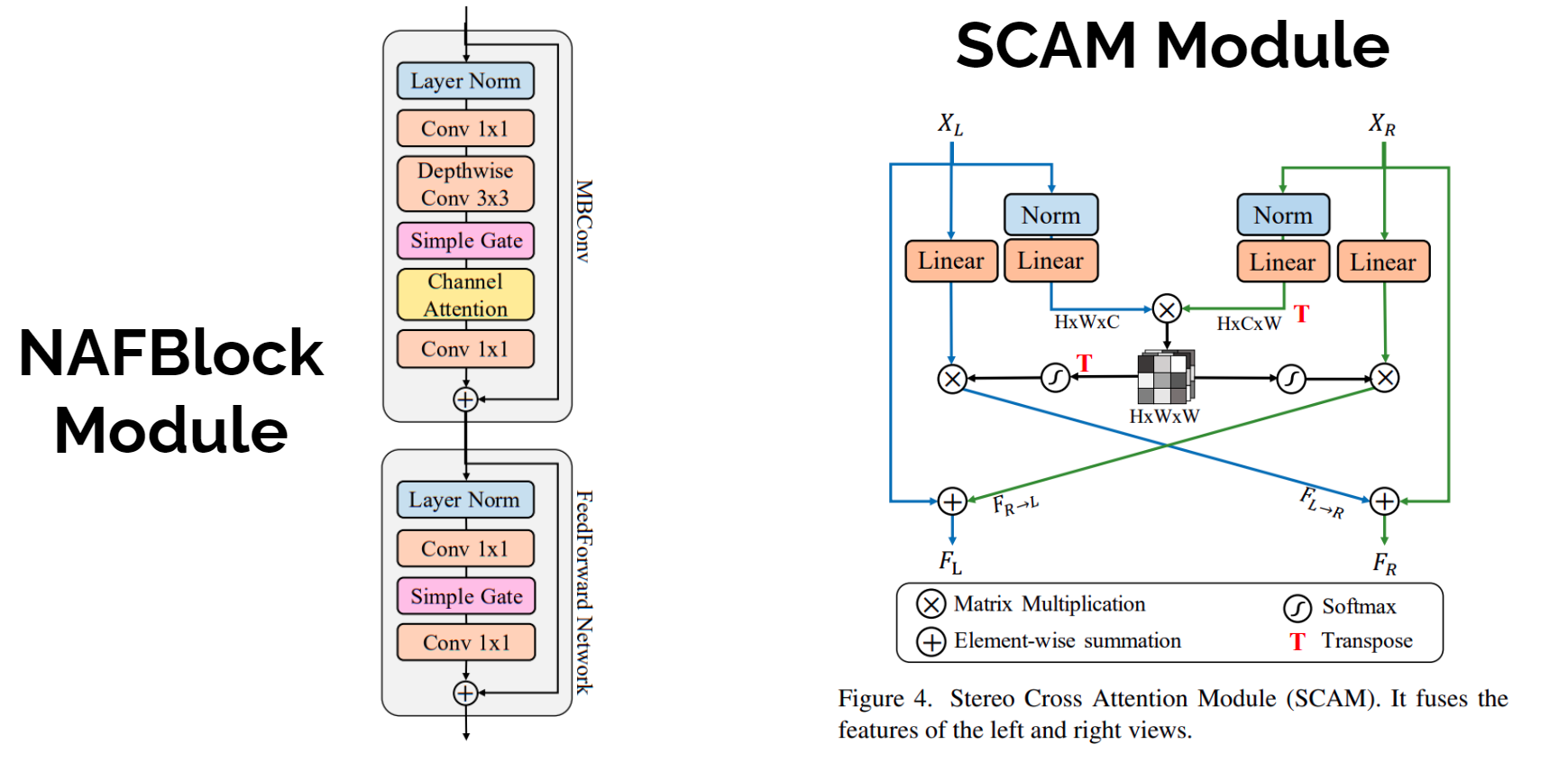
NAFSSR Model Architecture
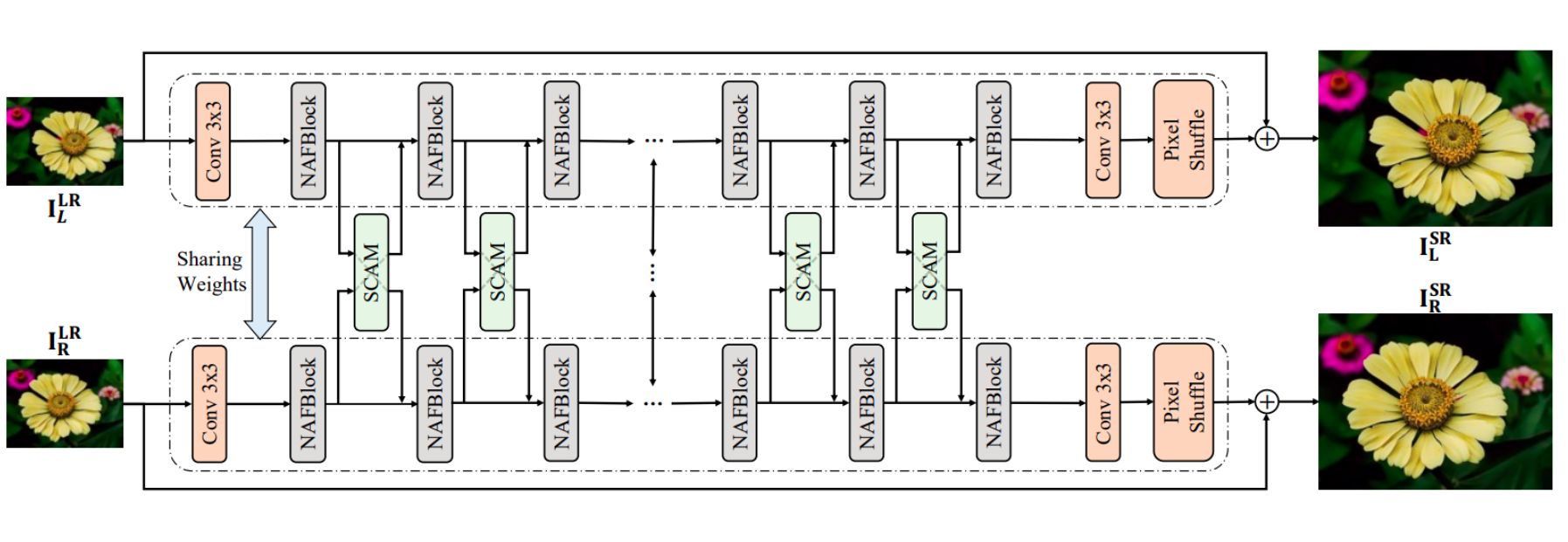
- NAFNet achieves competitive performance on single image restoration tasks with low system complexity and NAFSSR is a modification of the same.
- NAFNet blocks (NAFBlocks) extract intraview features for both views in a weight-sharing manner.
- NAFSSR adds simple cross attention modules to NAFNet so that it can fully utilize both intra-view information and cross-view information
- Stereo Cross-Attention Modules (SCAMs) are provided to fuse features extracted from the left and the right images.
- Training Strategies Used:
- Data Augmentation to Reduce Overfitting: Models were trained with small patches cropped from full-resolution images. These patches were randomly flipped horizontally and vertically
- Color Augmentation: RGB channels were shuffled randomly
- Regularizer: Stochastic Depth i.e. a subset of layers is randomly dropped and bypass them with the identity function.
- Loss: Pixel-wise L1 distance between the super-resolution and ground-truth stereo images
Perceptual Loss
- L1 Loss alone over-smoothens the output images, which is why better loss functions were required.
- Perceptual Loss: Used a pre-trained network VGG-16 to extract high-level features from SR and HR Images and compare them using some distance metric, like MSE.
- High-Level Features capture Perceptual Content of an Image (shape, composition, edges, colors, etc).
\(L_{percep} = || \phi(I) - \phi(I') ||^{2}\) - I and I’ are ground truth image and Generated Image respectively
- 𝜱 is a pre-trained VGG-16 that extracts high-level features
Texture Loss
- Texture loss using the gram matrix is a method for measuring the similarity of textures in deep learning-based image synthesis tasks.
- Texture loss is good at finding low level information such as texture features.
- We used a pre-trained VGG-19 and used outputs from mid-layers of the architecture.
Evaluation Metrics
- PSNR
- SSIM
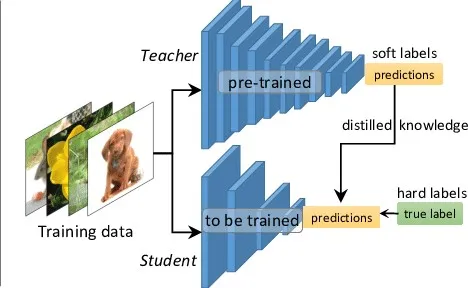
Student Teacher Model
- Large Models can’t be deployed much easily, limitations in size of model that can be loaded onto the GPU.
- But we also know that larger model of same architecture would clearly outperform a smaller model.
- Teacher acts as a supervisor and adds an additional loss term to enable student to learn faster.
- The Student is then able to learn better than what he was learning without the teacher.
- Performance is now somewhat in between the performance of lone student and lone pre-trained teacher.
- Note:
- Back Propagation, weight update only occurs in student, Teachers’ weights are left untouched
- Soft labels: predictions from pre-trained teacher model.
- Hard Labels: Ground Truths
Motivation
- We have two lead performers among all the model’s we tried:
Pre-Trained Large Model, trained only on L1 Loss.
- Our Trained Large Model, trained on combination of L1 Loss + Perceptual Loss + Texture Loss.
- The Training proceeds by taking patches of the train data.
- Testing Results showed that In 90% of the patches selected randomly from data our model outperformed better than Pre-Trained model.
- Selective Patches, showed better performance when processed with Pre-Trained Model.
Downside of Student-Teacher Model
- The two teachers will also require processing time on gpu.
- One way is to perform the forward propagation for the two teachers and the student in parallel, but that would optimally require 3 GPUs running in parallel.
- All three running on the same GPU result in repetitive context switching with respect to the models and this slows down the training speed a lot.
- On an 8-GB GPU, the expected training time reached till 53 days, for 4,00,000 iterations. We performed the training till 1L iterations, after which we switched to KLT-SRQA
Quality Assessment Based Losses
Method Used: KLTSR-QA. You can read more about the loss in detail from here
Achieved Rank 7 in Track1 and 13 in Track 2 Globally.
Publication Link